Role of the Various Micrornas in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Mahsa Fakeri1, Seyed Masoud Armandzadeh1, Fatemeh Shakoul1, Samad Sadigh Olyaei1, Elmira Aboutalebi Vand Beilankouhi1, Mohammad valilo2, Mohammad Reza Alivand3*
1Department of Animal Biology, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
2Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Medical Laboratories, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
3Department of Medical Genetics, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
- *Corresponding Author:
- Mohammad Reza Alivand
Department of Medical Genetics,
Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz,
Iran,
E-mail: alivandm@tbzmed.ac.ir
Received date:August 02,2022,Manuscript No.IPADO-22-14226; Editor assigned date:August 04,2022,PreQC No.IPADO-22-14226 (PQ); Reviewed date:August 16,2022,QC No. IPADO-22-14226; Revised date: August 26,2022,Manuscript No.IPADO-22-14226 (R) ; Published date: September 02, 2022, DOI: 10.36648/2471-8513.8.5.26
Citation: Fakeri M, Armandzadeh SM, Shakoul F, Olyaei SS, Beilankouhi EAV, et al. (2022) Role of the Various Micrornas in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Autoimmune Disord Vol.8 No.5: 26.
Abstract
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. It happens when the body's immune system targets its organs and tissues with producing a series of antibodies against nuclear and cytoplasmic antigens that cause inflammation and damage in various parts of the body. There are several factors including genetic and epigenetic involved in the development of this disease that lead to show various signs and symptoms in the body and MicroRNAs (miRNAs) is important one of these factors. miRNAs are small endogenous RNAs that play a pivotal role in regulating gene expression after transcription. The lack of regulation of miRNAs in many diseases causes the progression of these diseases. miRNA inhibitors and activators also have a many therapeutic strategies in the treatment of the variety of diseases such as lupus. Therefor in this review study, we discuss the role and function of miRNAs in lupus.
Keywords
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; miRNA; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; NF-κB; Toll-Like Receptor.
Abbreviation
NF-κB: NF-kappaB, TLR: Toll-Like Receptor, IFNY: Interferon gamma, SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, HIF-1a: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, ERK: extracellular signalregulated kinase, P13K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, AP-1: Activator Protein 1.
Introduction
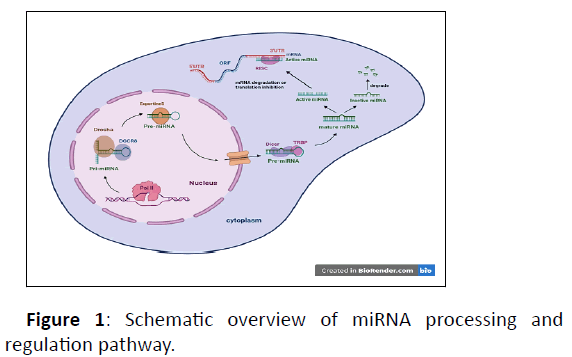
Certain cells with specific responsibilities in various levels and forms participate in the immune system response. They are made from stem cells in bone marrow under the influence of various types of cytokines. Peripheral blood leukocytes are the most diverse defense cells inside the body, generally including lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes [1-3]. Different lymphocytes originate from stem cells of the bone marrow. In human the production of B lymphocyte precursors in the embryo begins with the emergence organs such as liver as a Hematopoietic organ. In this period, liver is the most important that makes B cell precursors; However, when the bone marrow starts functioning, the production of B cells originates from the bone marrow. Humoral immunity is mediated by the production of antibodies. Antibodies with connecting to extracellular microbes “antigens” starting functions [1,4-6]. Beginner B cells residing in peripheral lymph follicles circulate among spleen, lymph nodes and Mucous lymphatic tissues in order to meet the antigens. Some B-cells affected by cxcl13, are called follicular Bcells; these lymphocytes' survival depends on cytokines such as BAFF. In some cases, the immune system responses can be induced against local antigens that cause several diseases called autoimmune diseases. Antigens activate autoantibodies in such diseases. Some mechanisms inhibit autoimmunity naturally and are called tolerance mechanisms. Autoimmune diseases infect all ages and are detectable and predictable by specific tests. Important factors play a role in the diseases among which genetic predisposition, environmental stimuli such as infections, and chemical and physical stress within the tissues can be named. SLE is considered as a chronic autoimmune disease that can infect a lot of organs in the body, particularly the skin, joints, blood, kidneys, and central nervous system. Most often, women get it especially in their productive years at the age of between 15 to 45. While the disease is more common in men before puberty and one out of five patients with lupus is a male [7-11]. Lupus is not a contagious disease but an autoimmune one that infects various parts of the body like joints, kidneys and skin, causing inflammation and swelling. The afflicted parts are painful and swollen. Lupus can be familial or hereditary. It may have different symptoms; chronic fatigue and vaginitis are the most common early symptoms [12]. Lots of children with lupus have intermittent or persistent fevers, weight loss and a loss of appetite. Some medications such as steroid and non-steroid anti-inflammatory ones are used to treat it. Some other medications, also, are used in severe forms of the disease such as cyclophosphamide. Genetic and epigenetic factors are two categories involved in SLE. Genetic symptoms such as miRNAs, Huston variation after translation, and miRNAs methylation can be named. miRNAs are small non-inhibitory ribonucleic acids that play an important role in regulating gene expression, RNA control, and post-transcriptional regulation [13]. Variations made in the expression of miRNAs can lead to many changes in the expression of different genes. miRNAs contain 18 to 24 nucleotides. Nowadays, attention has been paid to miRNAs studies in lots of human diseases such as various types of cancer, infections, chronic inflammation, and autoimmune diseases [14]. Some miRNAs are located inside the cell but some others are called circulating or extracellular miRNAs. Around 60% of human and other mammals' genes contain microRNAs. Disorders in miRNAs regulation can be due to viral or bacterial infections or Sex hormones. One of the important roles of miRNAs is controlling different aspects of the innate immune system, which can stimulate the production of cytokines and help deliver the antigens. The innate immune system is involved in autoimmune diseases such as lupus. miRNAs play an important role in the development of lupus. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus are more common among women than men, which may be due to estrogen. Estrogen can also control the expression of genes by regulating miRNAs. Studies have demonstrated that miRNA-155 and miRNA-181b are inhibited in women who have breast cancer cells. miRNAs are also present on the X chromosome, while no miRNAs have been detected on the Y chromosome yet. Since microRNAs play a role in B and Tcells' function and differentiation, we can conclude that they play an important role in autoimmune diseases and disorders. miRNAs dysfunction can cause several diseases like autoimmune diseases [15-20]. In the present study, we have explained and studied some miRNAs. MiR-326 is a type of miRNAs that has an important role in the production of TH17 [21,22]. Increase in the production of miR-326 can also increase the number of TH17 cells and its inhibition can decrease the number of TH17 cells. These miRNAs play an important role in various biological processes such as glucose and fat metabolism, puberty, differentiation of immune cells and cellular differentiation of TH17 cells. It can also be used as a therapeutic target in numerous types of cancer [22-24]. MiR-224 is another form of miRNAs found in mammals' X chromosome and is involved in apoptosis inhibition [25,26]. Mir-223 also has an important role in granulocytes differentiation and therefore, is a hematopoietic miRNA, this microRNA is suppressed in thyroid cancer [27,28]. MiR-146 is another microRNA, involved in NF-κB / TLR signaling pathway and is intergenic signaling path inhibitor which regulates inflammation procedure by increasing cytokine signaling [29,30]. MiR-21 also plays an important role in the function of B cells and the immune system, and is significantly increased in patients with HIV [31]. Our aim in the present study is to investigate the role of miRNAs in SLE. The mammals' genome is able to encode a large number of miRNAs. miRNAs are a precise regulator for biologic processes which are conducted after transcription. They can regulate and modulate a wide range of cellular activities and processes. These miRNAs play essential roles in regulating the immune system within the body [32,33]. When miRNA regulation is distorted, it causes some abnormalities and diseases inside the body, one of which is SLE [34]. miRNAs perform numerous tasks such as DNA methylation and Histone variations, all of which help cellular development and differentiation. So the relevant gene expression is controlled [35,36]. miRNAs containing primary transcriptions can produce different miRNAs that work in unison. There are two pathways for producing miRNAs inside the nucleus [37,38]. In the first pathway, RNA pol II transcribes the encoding genes and then they are capped and adenylated at their ends. Next, RNA changes into a loop called precursor miRNAs or pre-miRNAs. The stem in the RNA has approximately 33 base pairs and the upper loop size varies. Then, the primary miRNA or pre-miRNA is generated (Figure 1). In the second pathway, the primary miRNA is made from introns, which contain 65 nucleotides [39,40]. In this study, we analyzed some of miRNAs involved in immunity system and Lupus.
MiR-155
This miRNA has different significant roles in various physiological processes in human, is encoded by the host gene MiR-155 or MiR155HG. MiR155-5p performs significant role in cell differentiation because this miRNA in human is expressed in hematopoietic cells and CO34+, and keep these cells in the stem phase. Considering the research conducted, it has been shown that deficiency in pre-MiR-155 can cause insufficient growth and production of B and T lymphocytes. Therefore, presence of these miRNAs is very crucial for T regulating (T-reg) cells' development. It has also been observed that MiR-155 is overexpressed in many cases of cancer originating from B Lymphocytes. Thus, we can study this miRNA in such diseases a therapeutic target. The family related to this miRNA also plays a role in the immune system as a modulator, and it is involved in the immune system as a modulator for cellular and humoral immune responses. B and T cells, macrophages and activated dendritic cells increase the expression of MiR-155 [41-45].
MiR-181
MiR-181c, MiR-181-b, MiR-181a and MiR-181d are activated in humans by a gene called ERBB2, located in Chromosome 17. MiR-181 plays critical biological roles in human body. This miRNA also plays an important role in acute myeloid leukemia. It has been shown that MiR-181a enhances the differentiation of B Lymphocytes within the bone marrow [46-49].
MiR-146a
This miRNA plays an important role in the differentiation of immune cells. It has been shown that lack of MiR-146a increases the production of IFNY-producing lymphocytes. In addition, this miRNA can be rarely expressed in memory T cells. Moreover, this miRNA can be expressed in T-reg lymphocytes that maintain immune homeostasis. Studies have shown that in patients with lupus suffering from proteinuria, expression of MiR-146a is less than in those who do not have proteinuria. This miRNA can be decreased in connection with the lupus pathogenesis; when the expression of MiR-146a decreases, the type 1 interferon pathway is activated and causes some symptoms within the individual's body which is an indication of SLE [50-52].
MiR-142
Studies conducted on this miRNA have shown that shortages in MiR-142 can decrease T-reg. Therefore, the presence of this miRNA is crucial for the immune system, T lymphocytes growth and also the development of cellular and humoral immunity [53-55].
MiR-15a
MiR-15a makes the stem cells differentiate into megakaryocytes. Alongside MiR-155, it can make the T and Blymphocytes differentiate. Studies have shown the link between this miRNA and some cancers, one of them is gastric cancer [56,57].
MiR-21
This miRNA identifies cancer cells and its high levels act as an apoptotic agent. MiR-21 also plays a crucial role in the immune system, which can regulate T cell immunity. Therefore, in patients with lupus, the miRNA is overexpressed in T CD4+ lymphocytes [58, 59].
MiR-23b
This miRNA can prevent autoimmune diseases development by targeting some factors, and it can suppress IL17. It makes Blimp-1 expression suppressed and, thus, it can help regulate the antibody production; Therefore, acting as an antiinflammatory agent. The miRNA decreases in patients with lupus and Rheumatoid Arthritis [60,61].
MiR-29b
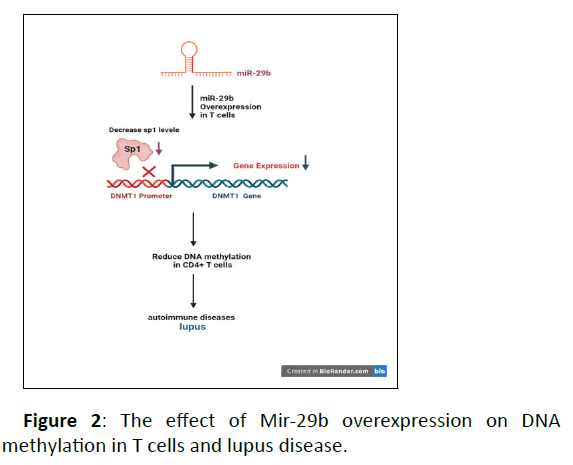
The expression of this miRNA is more than all other members of MiR-29 family. MiR-29b can be a biologic indicator of lupus. As the expression of the miRNA increases, a significant decrease in SP1 and DNMT1 proteins is observed. Therefore, T cells' methylation decreases which is a characteristic of SLE. That is because it has been observed in some studies that T cell DNA in individuals with lupus is reduced in methylation compared to healthy individuals (Figure 2). Studies have shown that there is a high amount of HIF-1a in the urine from patients with SLE, which is a key factor for inducing MiR-29. ERK 1/2 and P13K/AKT kinases can regulate the function of HIF-1a. It has been shown that the activation pathway of ERK 1/2 is impaired in patients with lupus. Therefore, all these factors demonstrate the role of MiR-29 in patients with lupus [62-64].
MiR-210
This miRNA plays numerous roles in most cells and performs various multipurpose tasks and functions, which include cease in DNA repair, cease in cellular proliferation, and suppressing mitochondria role. One of main roles of MiR-210 is to induce hypoxia, which is regulated by different factors. NFKB is a nuclear factor which can activate MiR-210. ATK also activates this miRNA. When T lymphocyte is activated, HIF-1a factor can be expressed and genes related to HIF-1a are activated. Various studies have shown the role of HIF-1a in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases alongside with the abnormal expression of HIF-1a factor and MiR210 in lupus [65-68].
MiR-183 cluster
MiR-183 cluster consists of 3 homologs named MiR-183, MiR-96 and MiR-182. Various studies have shown that these clusters play crucial roles, especially in some autoimmune diseases and cancer. Inhibition of these miRNAs reduces cell proliferation and invasions. This miRNA cluster can play an important role in cancers such as breast carcinoma, lung cancer and osteosarcoma. All members in the miRNA-183 cluster regulate several pro-inflammatory cytokines; therefore, they play a crucial role in the function of immune cells and the immune system. MiR-182 is an apoptosis regulator, which has antitumor activities. MiR-183 also is involved in tumor onset and development and is expressed abnormally in cancers. The miRNA is up-regulated in some cancers and is down-regulated in some others. Studies conducted on mice have demonstrated that the presence of miR-183 can be a treatment for lupus autoimmune disease and regulate T-reg levels and antibodies. It can extend mice's lifespan and lead to longer survival of mice with lupus. Regarding MiR-182-5p, it has been shown that the miRNA can contribute to lupus nephritis. FOX 01 expression prohibits kidney disorders in patients with lupus as a protective factor, but MiR-182-5p suppresses FOX 01 and leads the patients with lupus to impairment and fibrosis in the kidney [69-72].
MiR-17-92
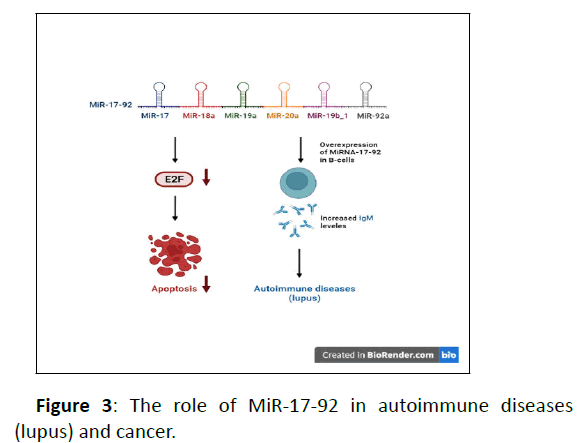
MiR-17-92 family plays important roles in the growth and differentiation of vertebrates. It has also been shown that improper mutation or regulation in these miRNAs can contribute to pathogenesis of various diseases such as cancer, autoimmune diseases and congenital growth defects. MiR-17-92 family codes six miRNAs named MiR-18a, MiR-17, MiR-19b-1, MiR-20a, MiR-19a and MiR-92a. Studies have shown that the MiR-17-92 cluster plays a basic role in malignancies and tumors such as breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, pancreatitis, prostate cancer, and stomach cancer. This miRNA family also, has a relation with some transcription factors, which regulate the cell cycle and apoptosis. E2F can be mentioned among the transcription factors related to this family of miRNAs, as you know E2F transcription factor, specifically E2F1 lead the cells to apoptosis. Therefore, the negative effects of MiR-17-92 on this transcription factor cause losses in E2F proteins' functioning. As a result, it reinforces the cells toward cellular dividing instead of dying. MiR-17-92 plays a major role in the immune system. Studies have shown that this family of miRNAs is involved in the differentiation of B cells and the production of IgM antibodies. Deletion of this miRNA also causes the removal of antibodies which are made against single-stranded and double-stranded DNA. If miRNA-17-92 is overexpressed for too long within lymphocytes, individuals will develop autoimmune and lymphoproliferative diseases. As you know, lupus is a sort of autoimmune disease in whose pathogenesis the family of MiR-17-92 may play a role [73-77] (Figure 3).
MiR-663
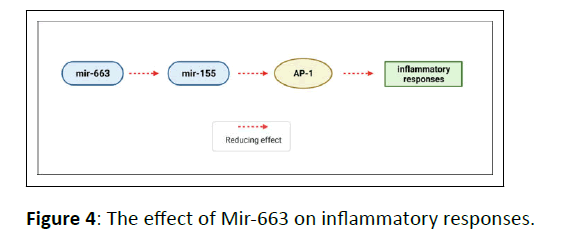
MiR-663 is a type of miRNA which is reduced in cardiovascular diseases and can act as a tumor suppressant. This miRNA can reduce the amount of miR-155 and therefore, decrease the inflammatory responses by reducing AP-1. On the other hand, studies have shown that MiR-663 activities are harmful in some diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, joint destruction, tumor erosion and cause their exacerbation. When the level of this miRNA increases, the gene expression is suppressed and the WnT signaling pathway is activated. Therefore, proinflammatory cytokines increase. MiR-663 plays an important role in lupus development through the reduction of the TGFB 1 secretion by T-cells [78-80] (Figure 4).
Conclusion
As mentioned, miRNAs are non-coding RNA sequences that are involved in regulating gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. This regulation of gene expression causes cells to function properly. Dysfunction of miRNAs has been proven in the development and progression of many diseases. Besides, improper expression of miRNAs in the immune system leads to many autoimmune diseases such as lupus. Therefore, our better understanding of the function of different types of miRNAs in autoimmune diseases such as lupus can provide us with many treatment strategies.
Future Perspective
Studies in recent years have shown that miRNA expression is altered in human autoimmune diseases, including lupus. Their dysfunction is also closely linked to many diseases, including autoimmune diseases. This dysfunction and regulation can be the result of various environmental factors such as sex hormones and viral or bacterial infections. Understanding the function of miRNAs in lupus and their role in the pathogenesis of this disease can provide researchers with many therapeutic strategies.
Acknowledgement
We thank the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences and Tabriz University for all support of this research.
Author Contribution
Mahsa Fakeri and Seyed Masoud Armandzadeh were involved in writing the article. Fatemeh Shakoul and Samad Sadigh Olyaei were involved in drawing the figures. Elmira Aboutalebi Vand Beilankouhi and Mohammad valilo were involved in data collecting. Mohammad Reza Alivand participated in the study design.
Funding
Authors declare that the study has no fund.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Chaplin DD (2010) Overview of the immune response. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125: 3-23.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhao E, Xu H, Wang L,Kryczek I,Wu K, et al. (2012) Bone marrow and the control of immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 9: 11-19.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Parkin J, Cohen B (2001) An overview of the immune system. Lancet 357: 1777-1789.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Bonilla FA, Oettgen HC (2010) Adaptive immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125: 33-40.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Seifert M, Küppers R (2016) Human memory B cells. Leukemia 30: 2283-2292.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Singh R, Soman-Faulkner K, Sugumar K (2022) Embryology, Hematopoiesis, in StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC, Treasure Island (FL).
- Liu S (2018) Release of Antibodies and Cytokines from B Cells. Methods Mol Biol 1868: 201-207.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Kato A, Hulse KE, Tan BK, Schleimer RP (2013) B-lymphocyte lineage cells and the respiratory system. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131: 933-957.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Lleo A, Invernizzi P, Gao B, Podda M, Gershwin ME (2010) Definition of human autoimmunity autoantibodies versus autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 9: A259-266.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Rosenblum MD, Remedios KA, Abbas AK (2015) Mechanisms of human autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 125: 2228-2233.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Schneider P (2005) The role of APRIL and BAFF in lymphocyte activation. Curr Opin Immunol 17: 282-289.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ocampo-Piraquive V, Nieto-Aristizabal I, Cañas C, Tobon GJ (2018) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 14: 1043-1053.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zan H, Tat C, Casali P (2014) MicroRNAs in lupus. Autoimmunity 47: 272-285.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Cammaerts S, Strazisar M, Rijk PD, Favero JD (2015) Genetic variants in microRNA genes: impact on microRNA expression, function, and disease. Front Genet 6: p. 186.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ratti M, Lampis A, Ghidini M, Salati M, Mirchev MB, et al. (2020) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as New Tools for Cancer Therapy: First Steps from Bench to Bedside. Target Oncol 15: 261-278.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Honarpisheh M, Kohler P, Rauchhaupt EV, Lech M (2018) The Involvement of MicroRNAs in Modulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis. J Immunol Res 2018: 4126106.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Teo AYT, Xiang X, Le MT, Li-Ann Wong A, Zeng Q et al. (2021) Tiny miRNAs Play a Big Role in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 13 : p. 337.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Li J, Wan Y, Ji Q, Fang Y, Wu Y (2013) The role of microRNAs in B-cell development and function. Cell Mol Immunol 10: 107-112.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ha TY (2011) MicroRNAs in Human Diseases: From Autoimmune Diseases to Skin, Psychiatric and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immune Netw 11: 227-44.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Garo LP and Murugaiyan G (2016) Contribution of MicroRNAs to autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 73: 2041-51.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Wei B, G Pei (2010) microRNAs: critical regulators in Th17 cells and players in diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 7: 175-181.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Huang J, X Xu, Yang J (2021) miRNAs Alter T Helper 17 Cell Fate in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol 12: p. 593473.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Chen B, Li H, Zeng X, Yang P, Liu X, et al. (2012) Roles of microRNA on cancer cell metabolism. J Transl Med 10: p. 228.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhao N, Wang Z, Cui X, Wang S, Fan C, et al. (2021) In Vivo Inhibition of MicroRNA-326 in a NOD.H-2(h4) Mouse Model of Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Front Immunol 12: p. 620916.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Huang Y, Li Y, Wang FF, Lv WG, Xie X, et al. (2016) Over-Expressed miR-224 Promotes the Progression of Cervical Cancer via Targeting RASSF8. PLoS One 11: p. e0162378.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Yuan K, Xie K, Fox J, Zeng H, Gao H,et al. (2013) Decreased levels of miR-224 and the passenger strand of miR-221 increase MBD2, suppressing maspin and promoting colorectal tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology 145: 853-864.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Gilicze AB, Wiener Z, Toth S, Buzas E, Pallinger E, et al. (2014) Myeloid-derived microRNAs, miR-223, miR27a, and miR-652, are dominant players in myeloid regulation. Biomed Res Int 2014: p. 870267.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Dai R, Ahmed SA (2011) MicroRNA, a new paradigm for understanding immunoregulation, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases. Transl Res 157: 163-179.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhou C, Zhao L, Wang K, Qi Q, Wang M,et al. (2019) MicroRNA-146a inhibits NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production by regulating IRAK1 expression in THP-1 cells. Exp Ther Med 18: 3078-3084.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Saba R, Sorensen DL, Booth SA (2014) MicroRNA-146a: A Dominant, Negative Regulator of the Innate Immune Response. Front Immunol 5: p. 578.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Wu X, Zhang LL, Yin LB, Fu YJ, Jiang YJ, et al. Deregulated MicroRNA-21 Expression in Monocytes from HIV-Infected Patients Contributes to Elevated IP-10 Secretion in HIV Infection. Front Immunol 8: p. 1122.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Bhaskaran M, Mohan M (2014) MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet Pathol 51: 759-774.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Luo X, Ranade K, Talker R, Jallal B, Shen N, et al. microRNA-mediated regulation of innate immune response in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 15: p. 210.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Yan S, Yim LY, Lu L, Sing Lau C, Sau-Fong Chan V (2014) MicroRNA Regulation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathogenesis. Immune Netw 14: 138-148.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Malumbres M (2013) miRNAs and cancer: an epigenetics view. Mol Aspects Med 34: 863-874.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Bianchi, M, Renzini A, Adamo S, Moresi V (2017) Coordinated Actions of MicroRNAs with other Epigenetic Factors Regulate Skeletal Muscle Development and Adaptation. Int J Mol Sci 18:840.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Morales S, Monzo M, Navarro A (2017) Epigenetic regulation mechanisms of microRNA expression. Biomol Concepts 8: 203-212.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C (2018) Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9: p. 402.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Achkar NP, Cambiagno DA, Manavella PA (2016) miRNA Biogenesis: A Dynamic Pathway. Trends Plant Sci 21: 1034-1044.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ying SY, Chang DC, Lin SL (2008) The microRNA (miRNA): overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol Biotechnol 38: 257-268.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Mashima R. (2015) Physiological roles of miR-155. Immunology 145: 323-333.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Elton TS, Selemon H, Elton SM, Parinandi NL (2013) Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes. Gene 532: 1-12.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Chandan K, Gupta M, Sarwat M (2019)Role of Host and Pathogen-Derived MicroRNAs in Immune Regulation During Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Immunol 10: p. 3081.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Raisch J, Darfeuille-Michaud A, Nguyen HT (2013) Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J Gastroenterol 19: 2985-2996.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Pashangzadeh S, Motallebnezhad M, Vafashoar F, Khalvandi A, Mojtabavi N (2021) Implications the Role of miR-155 in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol 12: p. 669382.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Indrieri A, Carrella S, Carotenuto P, Banfi S, Franco B (2020) The Pervasive Role of the miR-181 Family in Development, Neurodegeneration, and Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21: p. 2092.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zheng H, Liu J, Tycksen E, Nunley R, McAlinden A (2019) MicroRNA-181a/b-1 over-expression enhances osteogenesis by modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling and mitochondrial metabolism. Bone 123: 92-102.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Knarr M, Nagaraj AB, Kwiatkowski LJ, DiFeo A (2019) miR-181a modulates circadian rhythm in immortalized bone marrow and adipose derived stromal cells and promotes differentiation through the regulation of PER3. Sci Rep 9: p. 307.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Kim C, Ye Z, Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ (2021) miR-181a-regulated pathways in T-cell differentiation and aging. Immun Ageing 18: p. 28.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Rusca N, Deho L, Montagner S, Zielinski CE, Sica A, et al. (2012) MiR-146a and NF-κB1 regulate mast cell survival and T lymphocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 32: 4432-4444.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- So BYF, Yap DYH, Chan TM (2021) MicroRNAs in Lupus Nephritis-Role in Disease Pathogenesis and Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci 22: p.10737.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H, Ni X, Yuan M, et al. (2009) MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum 60: 1065-1075.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Scherm MG, Daniel C (2020) miRNA Regulation of T Cells in Islet Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 20: p. 41.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Wang WL, Ouyang C, Graham NM, Zhang Y, Cassady K, et al. (2022) microRNA-142 guards against autoimmunity by controlling Treg cell homeostasis and function. PLoS Biol 20: p. e3001552.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Dekkema GJ, Bijma T, Jellema PG, Den Berg AV, Kroesen BJ, et al. (2019) Increased miR-142-3p Expression Might Explain Reduced Regulatory T Cell Function in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis. Front Immunol 10: p. 2170.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhang L, Sankaran VG, Lodish HF (2012) MicroRNAs in erythroid and megakaryocytic differentiation and megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor lineage commitment. Leukemia 26: 2310-2316.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Edelstein LC, Bray PF (2011) MicroRNAs in platelet production and activation. Blood 117: 5289-5296.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ruan, Q, Wang P, Wang T, Qi J, Wei M, et al. (2014) MicroRNA-21 regulates T-cell apoptosis by directly targeting the tumor suppressor gene Tipe2. Cell Death Dis 5: p. e1095.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhang Z, Huang Q, Yu L, Zhu D, Li Y, et al. (2021) The Role of miRNA in Tumor Immune Escape and miRNA-Based Therapeutic Strategies. Front Immunol 12: p. 807895.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Chi M, Ma k, Li Y, Quan M, Han Z, et al. (2021) Immunological Involvement of MicroRNAs in the Key Events of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol 12: p. 699684.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhu S, Pan w, Song x, Liu y, Shao x, et al. (2012) The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat Med 18: 1077-1086.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Qin H, Zhu X, Liang J,Wu J,Yang Y, et al. (2013) MicroRNA-29b contributes to DNA hypomethylation of CD4+ T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus by indirectly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. J Dermatol Sci 69: 61-67.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Amodio N, Rossi M, Raimondi L, Pitari MR, Botta C, et al. (2015) miR-29s: a family of epi-miRNAs with therapeutic implications in hematologic malignancies. Oncotarget 6: p. 12837-12861.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Kourti M, Sokratous M, Katsiari CG (2020) Regulation of microRNA in systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of miR-21 and miR-210. Mediterr J Rheumatol 31: 71-74.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Dang K, Myers KA (2015) The role of hypoxia-induced miR-210 in cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci 16: 6353-6372.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Ivan M and Huang X (2014) miR-210: fine-tuning the hypoxic response. Adv Exp Med Biol 772: 205-227.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Zhang D, Cao X, Li J, Zhao G (2015) MiR-210 inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting DR6 in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 5: p. 12775.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Garchow B, Acosta MY, Kiriakidou M (2021) HIF-1α and miR-210 differential and lineage-specific expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Immunol 133: 128-134.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Dambal S, Shah M, Mihelich B, Nonn L (2015) The microRNA-183 cluster: the family that plays together stays together. Nucleic Acids Res 43: 7173-7188.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Xu S, Coku A, Muraleedharan CK, Harajli A, Mishulin E ,et al. (2020) Mutation Screening in the miR-183/96/182 Cluster in Patients With Inherited Retinal Dystrophy. Front Cell Dev Biol 8: p. 619641.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Cao D, Di M, Liang J, Shi S, Tan Q, et al. (2020) MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression. J Cancer 11: 1315-1324.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Wang X, Wang G, Zhang X, Dou Y, Dong Y, et al. (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-182-5p contributes to attenuation of lupus nephritis via Foxo1 signaling. Exp Cell Res 373: 91-98.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Mendell JT (2008) miRiad roles for the miR-17-92 cluster in development and disease. Cell 133: 217-222.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Concepcion CP, Bonetti C, Ventura A (2012) The microRNA-17-92 family of microRNA clusters in development and disease. Cancer J 18: 262-267.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Li H, Wu Q, Li T, Liu C, Xue L, et al. (2017) The miR-17-92 cluster as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of gastric cancer: evidence and literature review. Oncotarget 8: 45060-45071.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Xiang J, Wu J (2010) Feud or Friend? The Role of the miR-17-92 Cluster in Tumorigenesis. Curr Genomics 11: 129-35.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Kang SG, Liu WH, Lu P, Jin HY, Lim HW, et al. (2013) MicroRNAs of the miR-17∼92 family are critical regulators of T(FH) differentiation. Nat Immunol 14: 849-857.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Michaille JJ, Piurowski V, Rigot B, Kelani H, Fortman EC, et al. (2018) MiR-663, a MicroRNA Linked with Inflammation and Cancer That Is under the Influence of Resveratrol. Medicines (Basel) 5: p. 74.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Tili E, Michaille JJ, Adair B, Alder H, Limagne E, et al. (2010) Resveratrol decreases the levels of miR-155 by upregulating miR-663, a microRNA targeting JunB and JunD. Carcinogenesis 31: 1561-1566.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
- Geng L, Tang X, Zhou K, Wang D, Wang S, et al. (2019) MicroRNA-663 induces immune dysregulation by inhibiting TGF-β1 production in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol 16: 260-274.
[Crossref], [Googlescholar], [Indexed]
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences